
Beauty, elegance, vulnerability
The roe deer combines many virtues but also
generates significant damage to the crop fields.
Name
- Scientific name: Capreolus capreolus
- Spanish: Corzo
- Catalan: Cabirol
- Euskera: Orkatz
- Galician: Corzo
Classification
- Class: Mammals
- Order: Ungulates
- Family: Cervidae (deer)
- Species: Roe deer
Degree of protection of the roe deer
Worldwide
The roe deer is an abundant animal and is not protected.

In Spain
The roe deer is not protected and is a huntable species. This means that it can be hunted.
In Catalonia
Same as in Spain.
Roe deer distribution map
Distribution:
The roe deer is present in almost all European countries and also inhabits a part of Western Asia.
There is a population of roe deer inhabiting the area with high nuclear radiation in Chernobyl (Russia).
Roe deer habitat
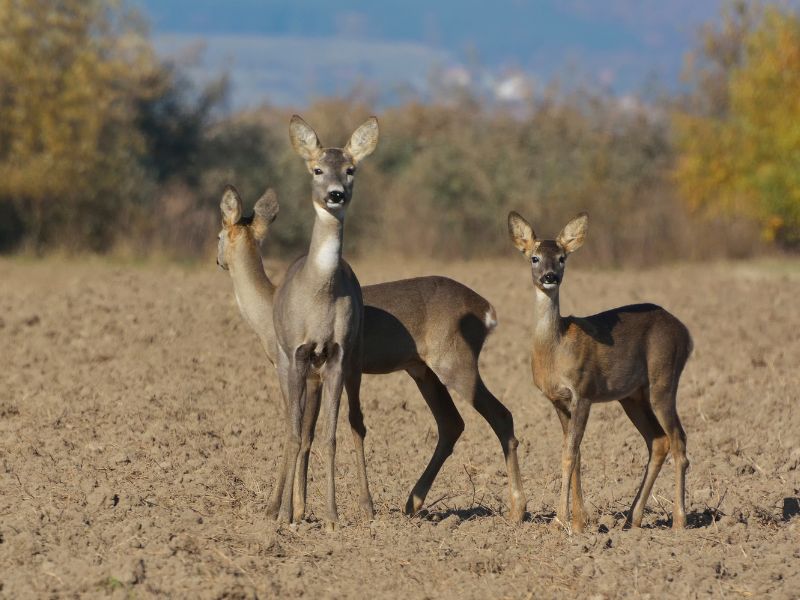

The roe deer has adapted to a wide variety of habitats: forests, open agricultural areas and even in high mountains.
Their population is increasing and they are moving closer and closer to the cities and towns.
Nutrition

Roe deer are herbivores
They feed mainly on grass, leaves, berries and young shoots. They are especially fond of very young and tender grass, which, unfortunately, causes significant damage to fields. They eat the sprouts of cereals and the plant, although it continues to grow, is left without grain.
How does the roe deer eat?
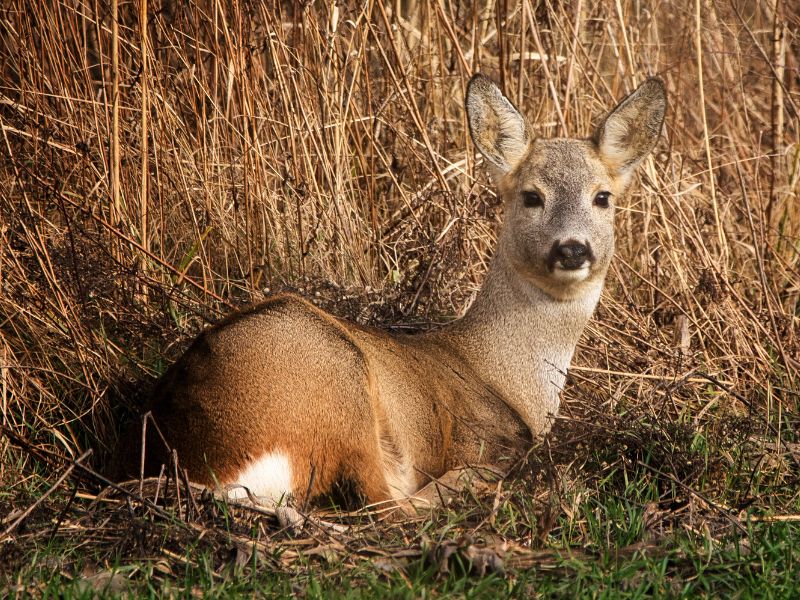

Roe deer are ruminants. This means that it cannot digest food at the first try.
It seeks quiet moments. It regurgitates small mouthfuls of food already consumed from the stomach into the mouth. It chews them and swallows them a second time.
Social life of roe deer
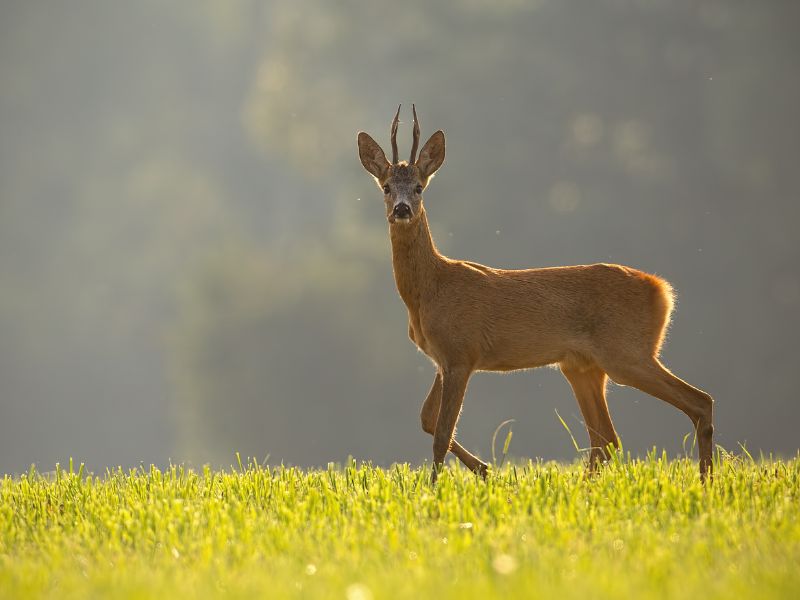

Solitary animals
Roe deer are solitary animals. But in times of food shortage, they group together. In open fields, up to 90 specimens can be observed together! In forests, the group usually does not exceed 15 animals.
Bellow
In July and August, males come into heat. They approach females, chase them and if they encounter another male they fight for the right to mate with the female.
Roe deer reproduction
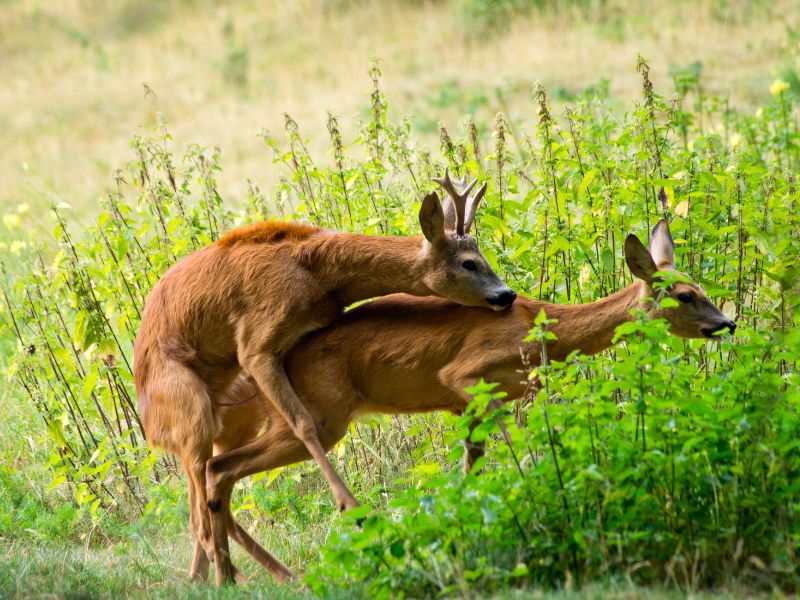

Deferred implantation
The young are born 10 months after mating. During the first 5 months the embryo does not develop. In December the embryo attaches to the uterine wall and begins to grow. The offspring is born in May.
Why do roe deer extend gestation time?
Males lose a lot of weight during the mating season. In summer, food is plentiful and they can easily recover their strength.
In the spring, new grass begins to sprout and the embryo begins to develop. Hatchlings are born in times of food abundance.
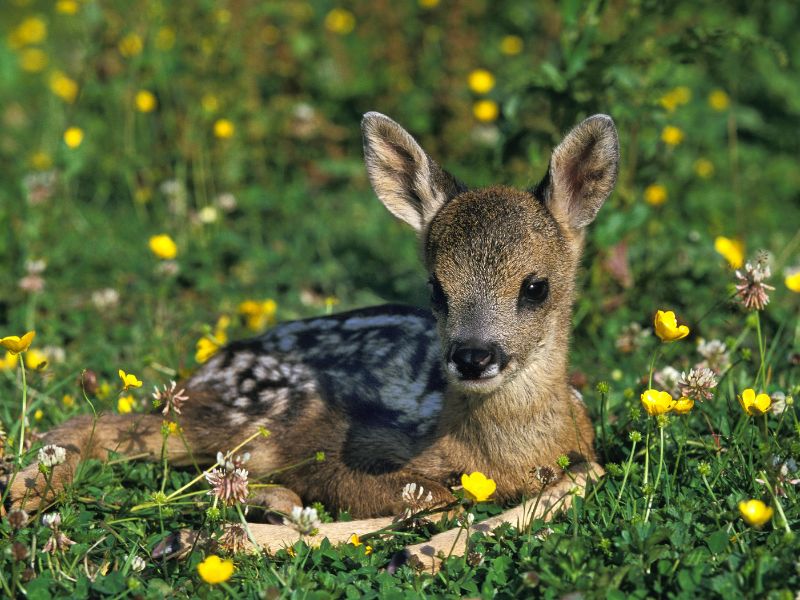
Roe deer fawns

In May, usually two offspring of opposite sex are born.
The mother leaves them alone, well hidden, and comes only to feed and clean them. At 3 weeks of age, they can run well and begin accompanying their mother.
If you find a small roe deer that looks weak, small, but shows no injury, don’t touch it. Roe deer fawns are like this. Get away from him as quickly and quietly as possible. Its mother takes care of it.
How many years can a roe deer live?
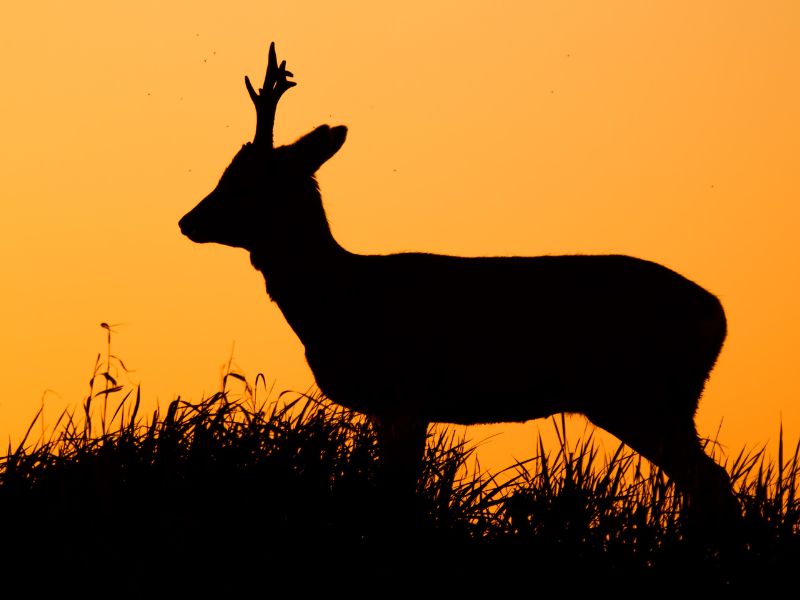

In the wild, they usually live 7 to 8 years. In captivity, exceptionally, up to 20.
Roe deer can reproduce as early as 1 year of age.
Offspring predators
- Foxes
- Wild boars
- Birds of prey
Predators of adult roe deer
- Human ( Roe deer are a huntable species )
- Wolf
- Lynx
- Bear
Identifying roe deer
The roe deer is the smallest of the European deer species.
They measure about 60 cm to their back (measured to the «withers») and weigh about 20 – 30 kg.
In summer its coat is reddish brown, in winter it is gray.
For the first 6 weeks of their life, fawns have white spots on their torso.
Horns
Only males have horns.
In autumn they fall off and new ones start to grow immediately.
During their growth, they are covered by a fine tissue (like velvet).
The horns are about 20 cm long and usually have 3 prongs.
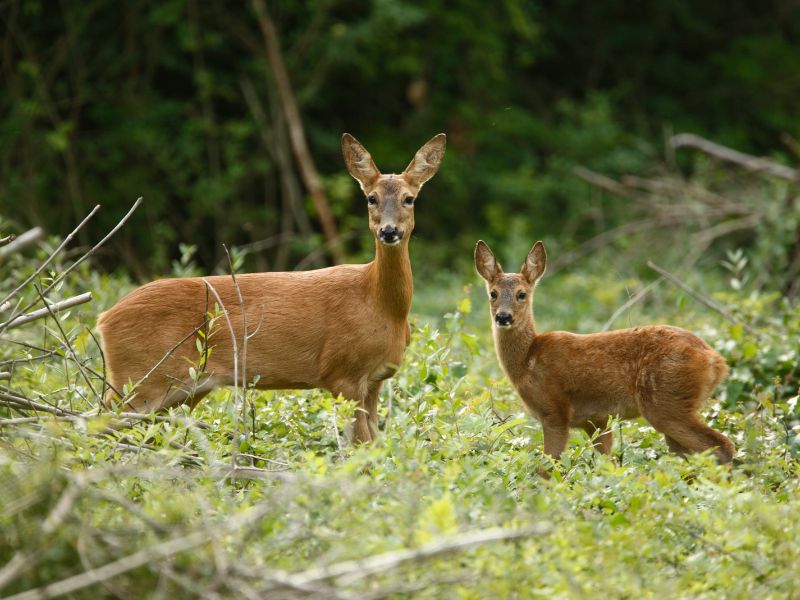




We must keep our eyes wide open when driving. Roe deer have to cross roads in search of food. Many end their lives as victims of a traffic accidents.
They will thank us with their beauty.